Details Are Part of Our Difference
Embracing the Evidence at Anheuser-Busch – Mid 1980s
529 Best Practices
David Booth on How to Choose an Advisor
The One Minute Audio Clip You Need to Hear
Category: Education
Rick’s Story…All Together Now

As dedicated readers know, over recent months we’ve published “chapters” of Rick Hill’s 50-plus years in the finance industry, and many of you have asked, “Can we get Rick’s entire story all in one place?” The answer is a resounding “of course!” So here it is…all together…Wharton Business School through founding Hill Investment Group. Stay tuned. Rick isn’t finished adding to his lessons.
Details Are Part of Our Difference
As our clients know, we seek to eke out every last basis point of potential return for you. So, while we balance the ideal combination of factors to achieve the highest odds of excess return, we also seek to minimize all costs, expenses, and taxes which eat into an investor’s net return. There are a couple of ways this plays out:
Evaluating Asset Managers
When evaluating asset managers, we scrutinize their trading practices to implement their strategies cost-effectively. If they don’t have reasonable trading procedures, their trading costs will be higher and, ultimately, lower the return of your investment.
Reducing Trading Fees
Just like our fund managers, we want to make sure that we are trading cost-effectively to be good stewards of your hard-earned capital. The most recent step in this effort was transitioning much of our recommended portfolio from mutual funds to ETFs, mainly to eliminate fees for trading mutual funds.
At Hill Investment Group, we are not satisfied with just better; we are always working towards finding the best solution we can find for you. The change from mutual funds to ETFs is a savings win, but we were eager to take it one step further.
Eliminating Hidden Costs
You may not know that ETFs have their own unique hidden trading costs. Like stocks, ETFs trade with a bid-ask spread. That means that, for example, market makers may buy an ETF at $9.99 and sell it to another investor for $10.01. The market maker earns a nice $0.02 profit/share, and the buyer and seller pay the cost.
We wanted to make this better. So, for ETF trades of over a certain size, rather than trade on the exchange with a limited short-term supply, we deal directly with the banks. We get the banks to compete for our business and bid against each other. This can shrink and nearly eliminate the market maker’s profit. This competition and direct access yield better prices than we could otherwise get on the exchange.
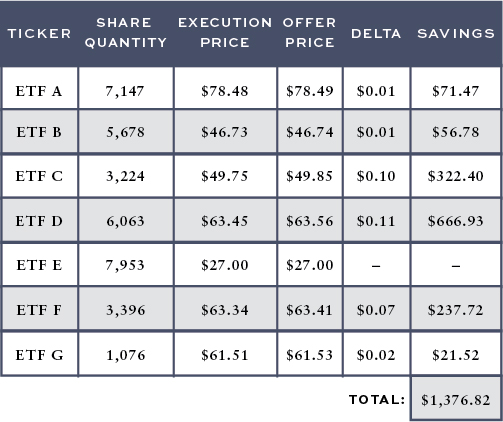
For example, we recently rebalanced one of our clients’ portfolios which resulted in purchases of various ETFs. The table above outlines the ETFs we bought, the price we would have gotten if we went to the market (Offer Price), and the price we executed at (Execution Price).
Conclusion: Details Matter
In just one day, using this trading strategy, we saved this client over $1,300 in trading costs. This one example is just one of many ways we fight for every basis point —the details matter and are part of the HIG difference.
Past results are not indicative of future results, or all client results. There are no implied guarantees or assurances that your target returns or cost savings will be the same as the example shown. Future returns or cost savings may differ significantly from the past due to many different factors. Investments involve risk and the possibility of loss of principal. The values and performance numbers represented in this report do not reflect management fees. The values used in this report were obtained from third-party sources believed to be reliable. Savings numbers were calculated by HIG using the data provided.
Founding Hill Investment Group – 2005

This is the latest in a series of posts from Rick. To see prior entries click here.
Once I’d experienced the benefits of an evidence-based investing approach myself, I started thinking about my clients back at the brokerage firm in 1967. How much better off would they have been if these tools were available to me, and in turn, them? With my newfound knowledge on how to truly help people, I decided to take the first step in realizing a dream. I left Anheuser-Busch in 1997, started earning my Certified Financial Planner (CFP) designation, and became a financial advisor at Buckingham Asset Management in St. Louis, Missouri
At Buckingham, I met Matt Hall, and after six years working together, we decided to start our own firm. Launching Hill Investment Group in 2005 allowed me to utilize everything I’d learned about both the evidence-based and emotional sides of investing. However, there were still important lessons ahead for me.
Like the best advisors, we always encourage our clients to focus on the long-term, not the market’s daily, weekly, or even yearly movements. Most people think “the long-term” means five or 10 years. However, as we discovered during the early days of Hill Investment Group, even a decade isn’t a significant amount of time in the grand scheme of a long-term investing strategy.
We couldn’t have known that we were launching our firm right in the middle of what’s now known as the “lost decade.” For the 10 years between 2000-2009, the S&P 500 had an annualized negative return of −0.95%*. Yes, the entire first decade of the 21st century netted a negative return as measured by the S&P 500.
The 2007-2008 financial crisis contributed to those poor results. An internationally diversified, evidence-based portfolio with exposure to small and value stocks helped our clients get through that period in great shape compared to investors focused on large-cap, U.S. stocks. What may be more important is what happened next: Between 2010 and 2019, all markets went on a sustained bull run, with the S&P 500 delivering a 13.6%* annualized return.
Talk about a huge swing over two consecutive decades. Even people who thought they were “long-term investors” might have reached the end of the lost decade thinking that their investment strategy wasn’t working and decided to change course. Doing so would have cost them dearly if they didn’t participate in the next decade’s rebound.
Lesson learned: The long-term is the rest of your life.
Sticking with a long-term investing plan requires discipline, including the discipline to weather a decade-long period of underperformance. Some people may focus on one goal or milestone to keep them on track, like wanting to retire at age 65. While that’s not a bad thing, the most successful investors are the ones who recognize that they’re working toward multiple financial goals—including significant expenditures during their working years like college costs and home improvements. To meet all these disparate goals, one must adopt a lifelong commitment to saving and investing through all market conditions. All of this is much easier with a trusted advisor…even better with a trusted team of advisors.
No one can accurately predict all the various things you might want to do with your savings 20, 30, or 40 years from now. Life throws all kinds of surprises our way. Some bad. Some fantastic. When you reach one long-term goal, new ones often magically emerge that become just as important to you. That’s why the real objective of one’s investment strategy should be to reach a point where there are opportunities to do almost anything you want for yourself, your family, and even for others.
I’ve witnessed how rewarding it can be for clients who embrace this approach. They’ve met the goals they set out to achieve for themselves with plenty left over to do some incredible things. Many of them are now supporting their grandchildren’s education or making charitable donations with their excess savings. One client’s wife was diagnosed with Alzheimer’s disease, inspiring him to provide major funding for Alzheimer’s research.
In other words, there will always be reasons to keep saving and investing. As long as you make good decisions based on what you can control, let the markets do what they’re going to do, and avoid meddling with your portfolio, you will likely have a lifetime to enjoy the results.
Improving your own investment experience
It’s easier than ever to start investing. You just need some money and a brokerage account or an app on your phone. The question is: will you be a gambler or an investor. There’s a huge difference.
Becoming a good investor isn’t easy. Many people struggle through experiences like the ones I’ve had myself over the past 50 years and never find a way to move past the stress and anxiety that they feel.
My hope is that these stories help you see how changing your attitude toward investing and the approach you follow can truly improve your quality of life. After all, that’s why people invest in the first place—to make their lives, and the lives of others, better. That’s the most important “return” you can achieve.
If you’ve followed along this far and are not a client already, I have one question:
How can we help you? Click here if you’d like to set up a time to talk.
*Returns data from https://ycharts.com/indicators/sp_500_total_return_annual. Past performance is not indicative of future performance. Principal value and investment return will fluctuate. There are no implied guarantees or assurances that the target returns will be achieved or objectives will be met. Future returns may differ significantly from past returns due to many different factors. Investments involve risk and the possibility of loss of principal. The values used were obtained from sources believed to be reliable.

