Details Are Part of Our Difference
Embracing the Evidence at Anheuser-Busch – Mid 1980s
529 Best Practices
David Booth on How to Choose an Advisor
The One Minute Audio Clip You Need to Hear
Category: Education
Picking Up Pennies – Volume 2
 Welcome to the second installment of picking up pennies. Last month, we discussed minimizing the cash in our client’s portfolios to maximize the return our clients get from their assets. Improving financial outcomes does not only come from maximizing investment returns, though. It also comes from minimizing taxes. This month, we will discuss asset location, what it is, how one can benefit, and how we use it.
Welcome to the second installment of picking up pennies. Last month, we discussed minimizing the cash in our client’s portfolios to maximize the return our clients get from their assets. Improving financial outcomes does not only come from maximizing investment returns, though. It also comes from minimizing taxes. This month, we will discuss asset location, what it is, how one can benefit, and how we use it.
- Volume 1 – Keep Cash Balances Low (Better Chance for Higher Returns)
- Volume 2 – Asset Location (Reduces Taxes)
- Volume 3 – Using ETFs (Reduces Taxes)
- Volume 4 – Trading ETFs in Competition (Reduces Trading Costs)
- Volume 5 – Number of Funds and Not Auto-Reinvesting Dividends (Reduces Trading Costs)
- Volume 6 – Tax Lots and Tax Loss Harvesting (Reduces Taxes)
- Volume 7 – Summary (Total Impact)
What is asset location?
Asset location is investing different types of assets (stocks vs. bonds) in various types of accounts (IRAs vs Trusts) to reduce overall taxes the investor pays over time.
The typical investor has three different types of accounts that are each taxed differently: IRAs (tax-deferred), Trusts (taxable), and ROTHs (tax-exempt). Since the investment gains from stocks and bonds are taxed differently, it is important to match the assets and accounts in a tax-optimal way.
How can asset location reduce taxes?
Taxable bonds (i.e., non-municipal bonds) are very tax-inefficient assets as they produce annual taxable income taxed at ordinary income rates (higher tax rates) rather than capital gains tax rates. If you hold bonds in a taxable account, you must pay those taxes year after year. Ultimately, this will reduce the dollar amount of investible assets that investors can earn a return on. Therefore, holding bonds in an IRA and deferring those taxes is preferred.
Stocks (particularly ETFs) are tax-efficient assets because most of their growth comes in the form of capital gains (lower tax rates) that you only need to pay when you sell the investment (not every year). If you hold stocks in an IRA, those gains will be taxed at ordinary income tax rates when you take distributions rather than capital gains rates. Thus, having stocks in a taxable account and paying the lower capital gains rate is preferred. Further, because stocks also tend to grow in value faster than bonds, if you have the option of a ROTH account, you would prefer to hold stocks in a ROTH account because you don’t pay any taxes on those gains nor their distribution from the account.
Let’s look at a simple example. Imagine an investor who wants to own 50% in stocks and 50% in bonds. In addition, half of their money is in an IRA, and half is in a taxable trust. Most advisors simply invest each account in the same 50/50 allocation. It is simple and easy to manage. You can buy software that automatically checks and rebalances the portfolio to these percentages.
Unfortunately, the above is not a tax-optimal solution. If we compare a lazy, uniform 50/50 solution to an asset location-optimized portfolio over a 30-year period, we’ll see a substantial difference in outcomes.
| 50/50 Each Account | Use Asset Location | |||||
| IRA | Taxable | IRA | Taxable | |||
| Bonds | Stocks | Bonds | Stocks | Bonds | Stocks | |
| Starting Value | $250k | $250k | $250k | $250k | $500k | $500k |
| Gross Final Value | $1.08M | $4.36M | $0.75M | $4.36M | $2.16M | $8.72M |
| After-Tax Final | $0.81M | $3.27M | $0.75M | $3.75M | $1.62M | $7.49M |
| Total: $8.58M | Total: $9.11M | |||||
Assumes 5% bond returns and 10% equity returns. Assumes a 25% income tax rate and a 15% capital gains tax rate.
With the same starting capital ($1M) and the same 50/50 overall allocation, an investor ends up with 6.2% more wealth over a 30-year investment period by using asset location effectively. This equates to 0.2% higher returns every year. This benefit will change for each investor based on their allocation and money in each type of account. The higher your tax rate, the more critical the optimal location becomes.
How does HIG use asset location?
We manage the allocation for all our clients at the household (highest) level rather than the account (lowest) level. By looking at the entire household, we can take advantage of asset location by putting assets like bonds and real estate in IRAs and high-growth assets like stocks in taxable and ROTH accounts. This way, we can ensure that each client has the correct allocation at the household level while being flexible at the account level to take advantage of the tax advantages of asset location.
We do this by creating a priority list for each type of account. We will put as many stocks as possible in a Roth, as much real estate and bonds as possible in the IRAs, and the overflow will be invested in the taxable accounts. Overall, investors don’t benefit from total investment returns; they care most about after-tax returns. Although care for asset location takes more time to manage, our commitment to picking up every basis point is part of a broader philosophy and commitment at Hill Investment Group. We understand that the little things, the pennies, add up to create meaningful gains for our clients. Through careful management and a relentless pursuit of opportunities, we believe these small gains will culminate in a substantial increase in overall returns.
This information is educational and does not intend to make an offer for the sale of any specific securities, investments, or strategies. Returns and market information quoted here was pulled from publicly-available, third-party sources believed to be accurate. Investments involve risk and, past performance is not indicative of future performance. Any actual return will be reduced by advisory fees and any other expenses incurred in the management of a client’s account. Consult with a qualified financial adviser before implementing any investment strategy.
Picking up Pennies

At Hill Investment Group, we’re dedicated to putting the odds for the best possible returns in your favor, leaving no basis point behind. Since every client is unique, the method to accomplishing this goal is multifaceted. I have talked to dozens of other prominent investment advisors about how they systematically handle these issues for their clients.
The answer I get 90+% of the time is some combination of, “We are not doing X because… it is too much work, clients don’t know the difference, the benefit is small, etc.”. As your fiduciary, that doesn’t sit well with us. Our obligation is to seek the best solutions we can find for our clients…no matter what.
Therefore, at HIG, we’ll continue to pick up the pennies. Over the coming months, we plan to highlight how we do that and what the impact can be on your wealth over time. We will discuss the following topics, starting with the level of cash we hold in our clients’ portfolios.
- Volume 1 – Keep Cash Balances Low (Better Chance for Higher Returns)
- Volume 2 – Asset Location (Reduces Taxes)
- Volume 3 – Using ETFs (Reduces Taxes)
- Volume 4 – Trading ETFs in Competition (Reduces Trading Costs)
- Volume 5 – Number of Funds and Not Auto-Reinvesting Dividends (Reduces Trading Costs)
- Volume 6 – Tax Lots and Tax Loss Harvesting (Reduces Taxes)
- Volume 7 – Summary (Total Impact)
Most investment advisors and hold between 5-10% of their client’s portfolios in cash for convenience. The “better ones” out there will hold 2-4% cash. Holding a large buffer of cash means the advisor can be a bit lazier in monitoring and trading client portfolios. This buffer comes at a cost. It’s called “cash drag” because, in general, cash doesn’t earn as high a return over time as investing in stocks or bonds. Therefore, for every $1 of cash you hold, there is an opportunity cost… which depending on how much cash you hold, could be massive.
We don’t want our clients to incur that cost, and thus, HIG keeps cash levels well below 1%, ideally around 0.5% (unless the client has recurring withdrawals). Maintaining cash levels below 1% requires diligence and a commitment to active monitoring. It’s easy to keep a significant amount of cash on hand, but it’s far more challenging—and ultimately rewarding—to deploy those funds into investments that generate meaningful returns.
We want the mutual funds and ETFs we invest in to embody the same approach. The average mutual fund holds between 3-5% cash, causing meaningful cash drag to their investors. The funds we recommend generally keep cash in the 0.1-0.3% range. By minimizing cash drag in your accounts and in the funds you hold, your portfolio more closely reflects the asset allocation and the corresponding risk profile you set up with us, that we agree to maintain on their behalf.
The impact of reducing cash drag can be significant. On average, stocks outperform cash by 6% annually. This means that an additional 5% in cash could lead to a 0.3% reduction in returns annually. While it might seem like a small fraction, due to compounding, the deficit can accumulate significantly over time. For every $1,000,000 invested, a 6.0% vs 5.7% return over 30 years represents a difference in wealth of ~$450,000.
At Hill Investment Group, our dedication to maximizing returns sets us apart. Our commitment to picking up every basis point is part of a broader philosophy. We understand that the little things, the pennies, add up to create meaningful gains for our clients. Through careful management and a relentless pursuit of opportunities, we believe these small gains will culminate in a substantial increase in overall returns.
Stay tuned for more insights in the coming months as we continue to share how these small gains add up to significantly impact our clients’ portfolios.
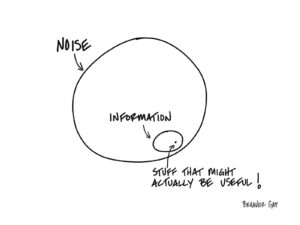
Noise Info Wisdom
Do me a favor.
Try to remember a time when you read or heard something about money in the news, you acted on it, and then, with the benefit of hindsight, you were glad you did.
This could include any number of things: the latest IPO, bear markets, bull markets, mergers, market collapses.
Go ahead, I’ll wait. Close your eyes and think about it.
I’ve done this experiment hundreds of times around the world, and I’ve only had one person come up with a valid example. It was news about a change in the tax law.
That’s it.
Isn’t that interesting?
Think of all the financial pornography out there, think of all the dental offices that have CNBC playing in the background, think of the USA Today Money section. Almost all of it is noise. Almost none of it is actionable.
Sure, every once in a while, there is this little teeny tiny speck of information that might be useful. But you sure have to wade through a lot of garbage to get to it.
This leads to one obvious question: Why are we paying attention to the noise in the first place?
It might be fun, if you’re into that kind of thing. You know, like going to the circus. But most likely, it’s just a waste of time.
What if, instead of obsessing over the news, you used that time to work on that list you have…
You know, “The List.” The one that has all the really important things you actually want to do with your time.
Doesn’t that sound so much better than spending another hour watching the news?

