Details Are Part of Our Difference
Embracing the Evidence at Anheuser-Busch – Mid 1980s
529 Best Practices
David Booth on How to Choose an Advisor
The One Minute Audio Clip You Need to Hear
Author: Hill Investment Group
Podcast Episode – Boring is Not Bad
A year out from the fear and uncertainty that caused the rapid pandemic-driven market crash of 2020, the financial media is back at it again with what they do best: spinning stories about the latest must-have investments. In this episode, Matt Hall explains why the boring route is the satisfying road to successful investing. Listen on Apple or click below.
Performance data discussed represents hypothetical past performance. This data is intended for educational purposes only and does not show the historical or expected results of any specific investor or Hill client. Data discussed is in US dollars. Indices are not available for direct investment and performance does not reflect expenses of an actual portfolio. Past performance is not a guarantee of future results. Current performance may be higher or lower than the performance discussed. The Investment return and principal value of an investment will fluctuate so that an Investor’s shares, when redeemed, may be worth more or less than their original cost.
Investing at the Top – A Forbes Piece We Love

John Jennings, podcast guest, Chief Strategist, and President at The St. Louis Trust Company, recently wrote about why it’s okay to invest at the top of the market in his latest Forbes piece. He shares the story of two clients, one that took his advice and one that didn’t. Which client are you…Smith or Jones? Read the outcome here.
What is a SPAC?
Have you heard about special purpose acquisition companies (SPAC)? Former NBA champion Shaquille O’Neal, former Speaker of the House Paul Ryan, hedge fund manager Bill Ackman, tennis legend Serena Williams, and former MLB player Alex Rodriguez all have one thing in common – they are all involved with SPACs. The hot new craze has caught Wall Street and celebrities buzzing, but should you care?
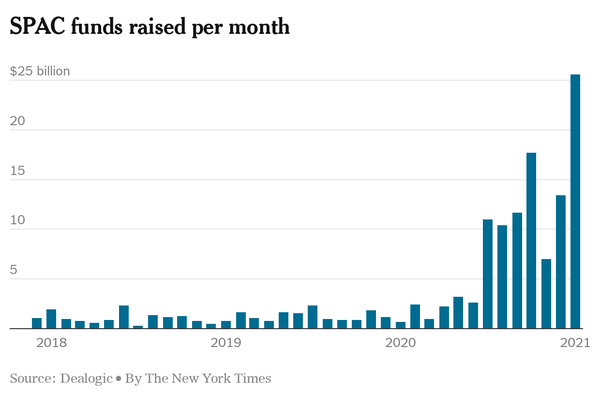
In 2020 we saw a resurgence in SPACs, as 248 new SPACs raised roughly $82 billion throughout the year, eclipsing the level from the previous decade. The SPAC boom has showed no signs of slowing down in 2021, as sponsors have raised nearly $26 billion in January alone, a monthly record.
SPACs, short for “special purpose acquisition companies”, are also sometimes known as “blank-check companies”. These companies are designed to raise funds through an initial public offering (IPO) in order to finance an acquisition, merger, or similar business combination with a private company. They often have no operating history of their own.
So, how do SPACs differ from traditional IPOs, the method in which many investors may be familiar with how companies go public? We can think of a traditional IPO as a company looking for money while a SPAC is money looking for a company.
SPACs tend to be quicker to market than traditional IPOs, as the process can take a few months, much shorter than the 24-36 month process for a traditional IPO. In addition to the benefit of speed, SPACs provide retail investors with early access, something not generally available in traditional IPOs, as shares are reserved for certain clients of the underwriting banks. For many SPACs, the sponsors/founders receive a 20% allocation, leading to a dilution in the company and potentially misaligned incentives. Because SPACs generally must use the money they’ve raised within two years or return it, they may be incentivized to get any deal done, regardless if it’s a good one.
What’s the bottom line? SPACs are simply another way for companies to raise capital and the public should be aware of the inherent pros and cons. Rather than being worried about missing out on the newest investment fad, most investors should work with their advisors to build a long-term plan that will help them achieve their financial goals. In other words, keep taking the long view.

